2018, Claflin College, Quadir's review: "Topamax 200 mg, 100 mg. Only $1,56 per pill. Cheap Topamax online OTC.".
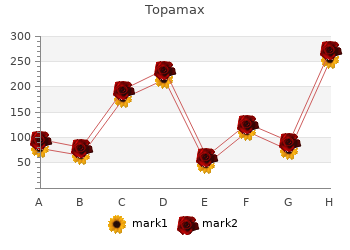
Finally topamax 200mg line, the decision was also based upon the interpretability and prevalence of the latent classes buy generic topamax 200 mg line. Likewise topamax 100mg without prescription, based on above mentioned criteria, the choice of best chronotype model in the substudy I fell on the four class model. Here, to confirm the choice of the four chronotype classes, the distributions in midpoint of sleep, a suggested measure of chronotypes (Roenneberg et al. The four classes differed, as was expected, in their midpoint of sleep and this was regarded as additionally supportive for the choice of a four-class chronotype classification in substudy I. Personal identifiers and possible dates of emigration or death for the Finnish former elite athlete cohort were obtained from the Population Register Centre of Finland. The proportional hazards assumption for each exposure was tested for by including an interaction with time in crude, univariate models. In table 2 the item-response probabilities that can range from 0 to 1 in each latent class are shown for men and in table 3 for women, respectively. Within each latent class, a certain pattern of responses is most likely or very unlikely to occur, respectively. Between the latent classes, certain class-specific item-response probabilities characterize the specific classes as compared to the others. The “Physically inactive, poor sleepers” is the least prevalent, fourth Profile in men (4. For each Profile, the characterizing highest probabilities in all variables are bolded and in italic. Furthermore, if an item response probability distinguishes the Profile from the others, the value is bolded and highlighted. The third Profile in women is called “Occupationally active, unsatisfied evening type sleepers” (17. The “Physically inactive, short sleepers” is the least prevalent, fourth Profile in women (10. For each Profile, the characterizing highest probabilities in all variables are bolded and in italic. Furthermore, if an item response probability distinguishes the Profile from the others, the value is bolded and highlighted. Members in Profiles 1 and 3 were younger than members in Profiles 2 and 4, and they had on average more educational years than members in Profiles 2 and 4. Highest prevalence of current smoking, as well as the highest alcohol consumption was observed for members in Profile 3. No significant differences were observed in weight between members of the Profiles. Men ”Physically “Lightly ”Occupation ”Physically Results of active, active, ally active, inactive, statistical normal morning evening type poor testing for range types with short sleepers” differences sleepers” normal sleepers” between range sleep” Profiles Profile number 1 2 3 4 Age, mean 46. Members in Profiles 1 and 3 were on average younger than members in Profiles 2 and 4, they had more educational years, and consumed on average more alcohol than members in Profiles 2 and 4. Women ”Physically ”Lightly ”Occupational ”Physically Results of active, active, ly active, inactive, statistical good normal unsatisfied short testing for sleepers” range evening type sleepers” differences sleepers” sleepers” between Profiles Profile number 1 2 3 4 Age, mean (years) 45. As was expected, the corrected midpoint of sleep in the four latent chronotypes differed, as follows: morning types, 2:49 a. This model suggested a division of chronotype into five latent groups, where one “tired, more evening type” and one “rested, more evening type” were identified. The characteristics of the “tired, more evening types” (17%) included not that easy to get out of bed in the morning, to be somewhat tired and have a not that good alertness in the morning and rate one-self as more evening- than-morning type, whereas the “rested, more evening types” (28%) were characterized by having quite easy to get up from bed in the morning, to be somewhat rested, but not having that good alertness in the morning, to rate oneself as more evening-than-morning type. The three other classes that were identified by the 5-class chronotype model included “morning types”, “rested, more morning types”, and “evening types”. The “morning types” (23%) were characterized by high likelihoods of having very easy to get out of bed in the morning, to be very rested and alert in the morning, and to rate oneself as definitely morning type. The “rested, more morning types” (24%) were characterized by having quite easy to get up from bed in the morning, to be somewhat rested and have a moderate alertness in the morning, to rate oneself as more morning- than-evening type and prefer morning working hours. The “evening types” (8%) were characterized by not that easy to get out of bed in the morning, to be somewhat tired and having very poor alertness in the morning, to report oneself as definitely evening type and to prefer afternoon working hours. The mean corrected midpoint of sleep in the five latent chronotypes differed, as follows: morning types, 02:48 a. When participants in working life were studied, similar associations were observed. However, after adjustments for age, smoking, alcohol consumption and education, as compared to membership in the “Physically active, normal range sleepers” Profile 1, only the association of membership in “Physically inactive, poor sleepers” Profile 4 with high HbA1c remained significant (Table 6). In women, most associations between membership in Profiles and high cardiometabolic risk factor levels were observed for membership in Profile 2 and Profile 4, as compared to Profile 1, respectively (Table 7). In men the membership in Profiles 2 and 4 was associated with a significantly higher risk score than membership in the Profiles 1 and 3, in both age-adjusted and fully adjusted models. In women, the Framingham 10-year Risk Score was highest for membership in Profile 2, differing from all other Profiles also in the fully adjusted models. Throughout the models was also membership in Profile 4 associated with a significantly higher risk score than in Profiles 1 and 3. Nevertheless, the interaction between history of sports and sleep duration or sleep quality regarding mortality was not significant and neither in former athletes or referents the sleep duration nor sleep quality were independently associated with mortality. Small gender differences between the Profiles were observed, but mainly the Profiles had similar characteristics in men as in women. Studying the operationalization of chronotype in the population-based sample, it was observed that chronotype classes are characterized by differences in morning- and evening preference and also morning tiredness. These Profiles were estimated to comprise of 45% and 47% of men and women, respectively. Epidemiological studies have previously observed physically active persons to report better sleep quality (Laugsand et al. Persons that report frequent insufficient sleep (Strine and Chapman, 2005) or insomnia-related symptoms (Haario et al.
Only methotrexate is seriously and sufficiently recog- nized as an initial drug for treating rheumatoid arthritis purchase topamax 200mg line. In addition buy topamax 200 mg cheap, one of the sulfur analogs of mercaptopurine buy 200 mg topamax otc, azathioprine, has been pro- posed as a cytotoxic drug, and it turned out to be more effective as an immunosuppressant. This is a possibly reason why it is advantageous over mercaptopurine as an immunosup- pressant. The mechanism of action of azathioprine as a cytotoxic drug is not different from the mechanism of action of other antimetabolites. Azathioprine is the primary drug used for transplants, especially for kidney transplants. However, azathioprine is useful in combination with cyclosporine, and it is even preferred in certain cases. Cyclophosphamide: Synthesis and properties of this drug are described in Chapter 30. Second, it kills proliferating cells, and evidently alkylates a certain region of 31. Finally, its action on T-cells is such that despite its overall suppressive effect, it can, in certain environments, suppress the response of these cells to antigens. Cyclosporine A: Cyclosporine A, [R-[R*,R*-(E)]]-cyclo-(L-alanyl-D-alanyl-N-methyl-L- leucyl-N-methyl-L-leucyl-N-methyl-L-valyl-3-hydroxy-N,4-dimethyl-L-2-amino-6- octenoyl-L-α-aminobutyryl-N-methylglycyl-N-methyl-L-leucyl-L-valyl-N-methyl-L-leucine) (31. A new era in the development of immunopharmacology began with the discovery of cyclosporines. Cyclosporines are produced by mycelial mushrooms Tolypocladium inflatum, Tricoderma polysporum, and Cylindrocarpon lucidum, which are found in the ground. Cyclosporine A is the first drug to affect a specific line of protecting cells of the body. Unlike usual cytotoxics, it suppresses T-cells and acts on all cell lines simultaneously. Cyclosporine A significantly eases the ‘reception’ of transplants, and increases the possi- bility of treating autoimmune system diseases. All cyclosporines (A,B,C, … U,V,W), are oligopeptides containing 11 amino acids closed in a cyclic form. All of these are known amino acids except the first, which some- times has not been isolated from natural sources. Because of all of the hydrogen bonds, the structure of cyclosporine is quite rigid. Cyclosporine A itself and a number of other cyclosporines have been completely synthe- sized. Many structural analogs have also been synthesized, and a few patterns have been discovered in terms of their structure and activity. It is known that the activity of the drug is determined by the entire cyclic structure, and not by its separate fragments. Likewise, it is also clear, that the structure of amino acids at position 1 is an important factor of 424 31. Despite the fact that the molecule is relatively large, cyclosporine eas- ily diffuses through the cellular membrane. It is possible that there are no corresponding ‘recognizing’ receptors for cyclosporine. However, there is a cytosol cyclosporine-binding protein known as cyclophilin, which has a molecular weight of about 15,000. Cyclophilins are observed mainly in T-cells; however, they are found in other tissues, in particular, in the brain and kidneys. Since the mechanism of action of cyclosporine is still being intensively studied, it must be noted that it is not cytotoxic in the general sense of the word, because it suppresses bone marrow function. Despite the fact that cyclosporine has not been used for a long time, it is the number one drug used for transplants. Cyclosporine is also being studied as a substance for treating a number of autoimmune diseases, including diabetes, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis. It also has had a great effect in treating schistosomia- sis, malaria, and filariasis. Despite the fact that all of these terms are basically interchangeable, the first three—antibiotics, anti-infectious agents, and anti- microbial drugs—are generally used to describe drugs used for treating infectious dis- eases, while the term chemotherapeutic drugs is more associated with drugs used for treating cancer. Antibiotics are essentially natural compounds produced by microorganisms that are capable of inhibiting growth of pathogenic microbes, bacteria, and a few of the more sim- ple microorganisms. Semisynthetic antibiotics generally are products that are a partially chemically altered versions of antibiotics that are isolated from natural sources. Thus, antibiotics are compounds produced by microorganisms and that are able to kill or inhibit growth of bacteria and other microorganisms. This definition makes a specific distinction between antimicrobial drugs produced by microorganisms and completely syn- thetic compounds. The difference is of a completely academic nature, and today the word antibiotic is used quite often for specifying antimicrobial drugs in general. It should be noted that there are compounds produced by microorganisms with antifungal and antitu- mor action, which also are classified as antibiotics. The general concept of antimicrobial action is called selective toxicity, which entails that the growth of the infected organism is inhibited or destroyed by certain drugs without harming host cells. All of the antimicrobial drugs used in clinical practice are selectively toxic with respect to microorgansisms. High selective toxicity of antibiotics to microor- ganisms is explained by the unique qualities of the organization of microbial cells, which are principally different from mammalian cells. The nature and degree of this selectivity determines whether the given antimicrobial drug is generally non-toxic in its relationship with mammalian cells or if it just exhibits certain toxicity on certain mammalian tissues.
By virtue of its presence in epithelial and endothelial cells cheap 100 mg topamax with visa, P-gp can also play a decisive role in the tissue and organ distribution of a drug generic 200 mg topamax with amex. Elucidation of these relationships is a critical goal certain to advance our knowledge and predictive ability order topamax 200 mg overnight delivery. However, the complexity underlying these relationships is likely to require technological advancements and a multi- disciplinary approach to solve. Investigation of P-gp and other efflux proteins promises to be a very fertile area of research in the years to come across a wide array of scientific disciplines. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Cell surface P-glycoprotein associated with mul- tidrug resistance in mammalian cell lines. Cellular localization of the multidrug- resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Immunohistochemical localization in normal tissues of different epitopes in the multidrug transport protein P170: evi- dence for localization in brain capillaries and crossreactivity of one antibody with a muscle protein. Direct demonstration of small intestinal secretion and site-dependent absorption of the beta-blocker talinolol in humans. Drug absorption limited by P-glycoprotein- mediated secretory drug transport in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cell layers. Modulation by verapamil of vincristine pharmacokinetics and sensitivity to metaphase arrest of the normal rat colon in organ culture. P-glycoprotein content and mediation of vincristine efflux: correlation with the level of differentiation in luminal epithelium of mouse small intestine. Evidence for intestinal secretion as an additional clearance pathway of talinolol enantiomers: concentration- and dose- dependent absorption in vitro and in vivo. Utility of Mdr1-gene deficient mice in assessing the impact of P-glycoprotein on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in drug discovery and development. Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. The complexities of hepatic drug transport: current knowledge and emerging concepts. Comparison of chromatographic and spectroscopic methods used to rank compounds for aqueous solubility. Differential induction of prehepatic and hepatic metabolism of verapamil by rifampin. Pharmacokinetic interaction of digoxin with an herbal extract from St John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum). P-glycoprotein: multidrug-resistance and a super- family of membrane-associated transport proteins. Internal duplication and homology with bacterial transport proteins in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene from multidrug-resistant human cells. Two members of the mouse mdr gene family confer multidrug resistance with overlapping but distinct drug specificities. Full length and alternatively spliced pgp1 transcripts in multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster lung cells. The inability of the mouse mdr2 gene to confer multidrug resistance is linked to reduced drug binding to the protein. Expression of the multidrug resistance gene product (P-glycoprotein) in human normal and tumor tissues. Functional role for the 170- to 180-kDa glycoprotein specific to drug-resistant tumor cells as revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Apparent stronger expression in the human adrenal cortex than in the human adrenal medulla of Mr 170,000– 180,000 P-glycoprotein. Multidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood-brain barrier sites. Classical and novel forms of multidrug resistance and the physiological functions of P-glycoproteins in mammals. The function of Gp170, the multidrug resistance gene product, in rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. Active secretion of drugs from the small intestinal epithelium in rats by P-glycoprotein functioning as an absorption barrier. Human P-glycoprotein transports cortisol, aldosterone, and dexamethasone, but not progesterone. Protein kinase C-independent correlation between P-glycoprotein expression and volume sensitivity of Cl-channel. The multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein modulates cell regulatory volume decrease. The role of P-glycoprotein and canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter in the hepatobiliary excretion of drugs. Basolateral localization and export activity of the human multidrug resistance-associated protein in polarized pig kidney cells. Methotrexate is excreted into the bile by canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter in rats. Congenital jaundice in rats with a mutation in a multidrug resistance-associated protein gene. Hereditary chronic conjugated hyper- bilirubinemia in mutant rats caused by defective hepatic anion transport.

8 of 10 - Review by V. Mezir
Votes: 45 votes
Total customer reviews: 45