The H1 receptors are easily solubilized and have been purified on lectin affinity columns order asacol 400 mg visa, indicating their glycoprotein nature purchase 400mg asacol fast delivery. H2 receptors are localized to the cortex and striatum and are found in neurons buy 400mg asacol, glial cells (astrocytes), and blood vessels. Thus the role of the central histamine receptor may not be information transmission, but sensitization of brain areas to excitatory signals from “waking amines. H3 receptors have been described and seem to be localized in cortex and substantia nigra; these seem to be presynaptic autoreceptors, controlling histamine release and synthesis. They are activated by histamine concentrations that are two orders of magnitude lower than those necessary for triggering postsynaptic receptors. Their blockade may potentially lead to increased blood flow and metabolism combined with a central arousal, whereas their stimulation (or inhibition of central H2 receptors) could have a sedative effect. Histamine-mediated hypothermia, emesis, and hypertension have been shown to exist, and the well-known sedative effects of H1 antihistamines are centrally mediated. Large alkyl groups on C-4 decrease activity and lead to partial agonists, whereas side-chain N-substitution enhances the antagonistic properties of the molecule. It is a selective H2 agonist, having between 19% and 70% H2 activity, with no effect on the H1 receptor. The circulatory effects are manifested as arteriolar dilation and increased capillary permeability, causing plasma loss. The localized redness, edema (hives, wheal), and diffuse redness seen in allergic urticaria (rash) or physical skin injury result from these circulatory changes. Humans and guinea pigs are very prone to bronchoconstriction by histamine (an H1 effect), and severe asthmatic attacks can be triggered by small doses, provided the person suffers from asthma and is therefore very sensitive to histamine. Stimulation of gastric acid secretion is the most important H2 response; it is blocked only by H2 antagonists. As mentioned before, the hormone gastrin may be involved in histamine release, because H2 antagonists block gastrin-induced acid secretion. H3 receptors are involved in mediating the neuroregulatory influence of the brain on stomach, lung, and heart. Replacement of the amino group with bioisosteric polar cationic groups yields imetit (4. They do not bear any close resemblance to the agonist since their binding involves accessory binding sites. Ethylenediamines, aminoalkyl ethers, and aminopropyl compounds, for which X is nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon, respectively, show a general H1 antagonist structure. The theophylline derivative was originally added to counteract the drowsiness produced by diphenhydramine, since it is a central excitant related to caffeine. They are quite polar molecules and therefore cannot cross the blood–brain barrier to reach central histamine receptors. One of the compounds that showed weak H2-antagonist activity, guanyl- histamine, was the point of departure in the development of these drugs. Extension of the side chain was found to increase the H2-antagonist activity, but some agonist effects were retained. When the very basic guanidino group was replaced by the neutral thiourea, burimamide (4. Introduction of the electron-withdrawing sulfur atom into the side chain reduced the ring pKa. The proportion of the cationic form was also decreased, and the tele tautomer became predominant. Reduced ionization improved the membrane per- meability of the molecule; the oral absorption of the resulting compound, metiamide (4. However, metiamide still showed some side effects in the form of hema- tological and kidney damage, which were attributed to the thiourea group. A satisfactory replacement was found by substituting another electron-withdrawing group on guanidine while retaining the appropriate pKa. It then became clear that an imidazole nucleus was not absolutely necessary for H2-antagonist activity. Treatment of peptic ulcers is a complicated and multilevel therapy in which H2 antagonists are very successful and widely used (and abused). Peptic ulcers may affect either the stomach (gastric ulcers, less common overall but more common in people with iatrogenic [i. This mucosal damage is promoted by Helicobacter pylori bacteria that colonize the gastric lining. To facilitate healing, prevent ulcer recurrence, and relieve pain, the medicinal chemistry approach is multipronged and involves lowering aggressive acid output, augmenting the mucous-based protection, and/or eradicating the Helicobacter pylori. The concentration of acid in the stomach may be reduced either by neutralizing the acid or by inhibiting acid production. The next major class of drugs for peptic ulcer disease is the mucoprotectants and other protective agents. Finally, since the microorganism Helicobacter pylori plays an important role in the pathogenesis of ulcers, antibacterial agents such as amoxicillin (4. The nonsurgical treatment of peptic ulcer is a superb example of how multiple mole- cular approaches can be used to therapeutically attack a single clinical problem from multiple directions. Also, the medical management of peptic ulcer disease demonstrates how antagonists of neurotransmitter messenger molecules (acetylcholine, histamine) can be used to treat nonneurological disorders. The role of β-adrenergic agonists and antag- onists in the treatment of cardiopulmonary diseases is a similar example.
It is possible to have a drug-drug interaction that is confined to the intestine during first-pass extraction 400 mg asacol fast delivery. Another important consideration for understanding metabolically based drug-drug interactions is that the level of exposure of the liver and intestinal mucosa to an inhibitor or inducer need not be identical (as discussed above) buy discount asacol 400 mg on line, particularly during the periabsorptive phase safe 400mg asacol, when modulator concentration at the intestinal mucosa may be much greater than that in the portal blood. It is also important to recognize that the intracellular mechanism underlying an interaction (e. Consequently, the extent of induction or inhibition at each site of metabolism/transport following acute or chronic administration of an interacting drug could be quite different (e. In the remainder of this chapter, we review the characteristic features of drug interactions that involve modulation of the first-pass intestinal metabolism of orally administered drugs. A full complement of drug-metabolizing enzymes is expressed in the human intestinal epithelium. The most important phase 1 enzymes in the context of drug-drug interactions are the cytochrome P450 enzymes. The specific P450 content of microsomes isolated from mucosal epithelium of the human proximal small intestine is roughly one-sixth to one-eighth of that found in liver microsomes (8,9). Notable aspects of drug interactions involving each of the aforementioned enzyme classes will be presented in the following sections. Mucosal enzyme concentration is greatest within the duodenal and jejunal sec- tions of the small intestine and declines distally and proximally. In a later study of 20 full-length intestines and livers from organ donors, Paine et al. A villous fraction consisting of mainly mature enterocytes was isolated from the intestinal samples. In this respect, these cell lines may represent an excellent model for xenobiotic metabolism in the human colon and its role in chemical-induced mutagenesis or cytotoxicity. Although some of this extreme variability in the latter study could be the result of events pre- ceding the procurement of tissue (i. Given the inaccessibility of the intestinal site of metabolism, it is understandable that most of the in vivo evidence is indirect in nature. The usual approach is to assume that systemic clearance represents hepatic clear- ance for drugs that are extensively metabolized, and that intestinal metabolism does not contribute to systemic clearance. For most drugs that are readily released from the oral formulation and have high intestinal permeability, Fa is often assumed to be unity. The assumption that intestinal mucosa does not contribute to systemic clearance (i. However, the entire dose released from the dosage form is exposed to the mucosal enzymes during its obligatory passage through the intestinal epithelium and, thus, the more relevant comparison is the intracellular enzyme concentration and intrinsic clearance (i. In studies that offer comparative metabolic kinetics between hepatic and intestinal (duodenal or jejunal) microsomes, mean intrinsic clearance for intestinal microsomes varied from 20% to as high as 200% of that for liver microsomes; the list of drugs include cyclosporine (41), eryth- romycin (15), indinavir (44,45), irinotecan (46), lovastatin (48), midazolam (8), quazepam (50), rifabutin (51), saquinavir (53), and tacrolimus (55). For many of these drug substrates, mucosal intrinsic clearances are comparable to the cor- responding mean hepatic intrinsic clearance. Whether there will be a similar intestinal and hepatic first-pass extraction for the aforementioned drugs is more difficult to predict since intestinal first-pass extraction is dependent on a number of other factors, including total oral dose, rate of drug absorption, enzyme saturability (Km), the absorptive region, mucosal barrier permeability, and binding to blood components. For example, should the dose be high enough to cause enzyme saturation, it is possible that a drug with a high hepatic and intestinal intrinsic clearance could largely escape intestinal first-pass extraction but not hepatic extraction. Also, if the basolateral membrane represents the rate-limiting barrier to the passage of drug across the intestinal epithelium, the residence time of the drug substrate within the enterocytes would increase and result in a greater metabolic first-pass loss than a comparable substrate with better permeability (6,68). A number of studies have shown that induction of midazolam elimination is highly route dependent (75–77). Although systemic clearance (Cl) of midazolam was also induced by rifampin, the effect was modest by comparison; i. This rem- arkable route dependency in the induction of midazolam clearance can be explained by induction of sequential first pass at the intestinal mucosa and the liver after oral administration, whereas only hepatic extraction is operative and inducible after intravenous administration. It should also be appreciated that the increase in systemic or hepatic clearance of midazolam following rifampin is limited to some extent by the ceiling of liver blood flow, as hepatic extraction of midazolam is increased from around 0. The inductive effects at the two sites appeared not to be concordant; in fact, the extent of induction was high at either the hepatic or intestinal site, but not both. Of note, all the drugs listed for which unambiguous data are available exhibit incomplete oral bioavailability. In addition, where both intravenous and oral administration have been studied, rifampin appears to increase the extent of intestinal first-pass metabolism and decrease intestinal bioavailability substan- tially; for example, alfentanil, Fgm ¼ 0. John’s wort, a widely used herbal supplement for the treatment of mild to moderate depression, has also attracted considerable interest. John’s wort on intestinal extraction was slightly greater than that on hepatic extraction. The difference can be attributed to the much higher peak cir- culating rifampin concentrations (8 mM) (86), compared with that of hyperforin (0. There is evidence indicating that micro- somal enzyme inducers can simultaneously act as inhibitors. These investigators proposed that the inductive effect of rifampin was masked by its simultaneous inhibition of repaglinide metabolism when repaglinide clearance was assessed immediately after concurrent rifampin administration when the circulating concentration of rifampin was high. The inductive effect of rifampin was fully revealed after the washout of rifampin by 24 hours. It stands to reason that the masking of an inductive effect by simultaneous inhibition is more likely to occur with intestinal first-pass metabolism; however, supportive evidence is lacking. The interplay between induction and inhibition also means that the outcomes of interaction studies with enzyme inducers may depend on study design; that is the relative timing of the inducer and substrate administrations. Although some of the pharmacokinetic changes observed were surely the result of an interaction in the liver, it is likely that the enzyme/ transporter barrier at the intestinal mucosa was also affected by ketoconazole. These interactions can conveniently be grouped according to the mechanism of inhibition, namely those involving reversible (i. For example, in an earlier study of the interaction between ketoconazole and tirilazad, Fleishaker et al.
Acyclovir has also been used success- fully during pregnancy to treat varicella pneumonia asacol 400 mg line, disseminated herpes infection cheap asacol 400 mg without a prescription, and herpes hepatitis (Johnson and Saldana discount asacol 400mg online, 1994; Petrozza et al. Recently, acyclovir has been used during the last 4 weeks of pregnancy to pre- vent recurrent herpes infections and prevent the need for cesarean delivery (Scott et al. Ganciclovir is more toxic than acyclovir, and there is no information regarding its use during pregnancy. Some of the maternal side effects secondary to the drug are difficult to distinguish from those caused by the disease process itself. None of these drugs has been adequately studied during human pregnancy, but clearly the benefit (life-saving) of their use outweighs any theoretical risk. Idoxuridine Idoxuridine is an ophthalmic antiviral agent used primarily for the treatment of herpes simplex eye infections. To date, there have been no reports of congenital anomalies in Antiparasitics 41 infants born to women treated with this agent during pregnancy, but there have been no adequately controlled scientific studies in humans. Idoxuridine has been reported to be associated with both eye and skeletal malformations in the offspring of pregnant rabbits who received this local antiviral agent in usual human doses (Itoi et al. Amantadine Amantadine is an antiviral agent used in the treatment and prophylaxis of influenza. However, this particular agent was not shown to be teratogenic in rats or rabbits. Pandit and associates (1994) did report that one of four fetuses exposed to amantadine had tetralogy of Fallot. Hillard and colleagues (1982) reported on the use of this drug late in pregnancy for dis- seminated herpes simplex infections. Although there are no reports of congen- ital abnormalities in well-controlled human studies, ribavirin has been reported to cause a variety of congenital anomalies in commonly used laboratory animals (Ferm et al. Other antivirals Other antivirals (idofovir, docosanol, famciclovir, penciclovir, foscarnet, valganciclovir, osteltamivir, zabamivir) have not been studied during pregnancy, or assessed for the pos- sible association with birth defects following use during the first trimester. Metronidazole, the only effective antiparasitic agent for tri- chomoniasis, has already been discussed (p. Of these, lindane (cream, lotion, or shampoo) is probably the most commonly used agent for both mites and lice. According to its manufacturer, lindane was not teratogenic in a variety of animals, although there are no adequate human reproduction studies. Lindane may be related to an increase in stillbirths in some animal studies (Faber, 1996). However, lindane may be absorbed systemically, which on rare occasions may lead to central nervous system toxicity (Feldman and Maibach, 1974; Orkin and Maibach, 1983). Although this adverse effect could also theoretically occur in the fetus, it would appear to be very unlikely and to date has not been reported. Antihelmintics Several antihelmintics are available to treated infested women, although it is usually not necessary to treat helminth infections during pregnancy. Both mebendazole (Vermox) and thiabendazole (Mintezol) are effective for a variety of helminths, including pin- worms (enterobiasis), whipworm (trichuriasis), roundworm (ascariasis), and hookworm (uninariasis). According to their manufacturer, none of these drugs was teratogenic in laboratory animals, although there are no adequate human reproduction studies. Pyrantel pomoate (Antiminth) is used primarily for the treatment of roundworm and pinworm. Although this agent has not been shown to be teratogenic in animals, there are no adequate studies in humans. Chloroquine is the pri- mary drug used for the treatment of malaria, as well as for chemoprophylaxis in preg- nant women who must travel to endemic areas (Diro and Beydoun, 1982). Although there have been no studies of infants whose mothers were treated for malaria during pregnancy with chloroquine, one study reported no increased frequency of congenital anomalies among 169 infants whose mothers received weekly low doses of the drug for malaria prophylaxis during pregnancy (Wolfe and Cordero, 1985). Quinine is used Special considerations 43 primarily for chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria. Although there are no large studies regarding its use during pregnancy, increased malformations have been reported when large doses were used to attempt abortion (Nishimura and Tanimura, 1976). Quinine sulfate tablets have also been utilized for leg cramps, but their efficacy is unproven. Although not recommended for the treatment of leg cramps during preg- nancy, the antimalarial quinines should not be withheld in the seriously ill pregnant woman with chloroquine-resistant malaria. Pyrimethamine, spiramycin, and sulfadiazine These agents are used primarily to treat toxoplasmosis. There are no adequate scientific studies of its use during pregnancy, but Hengst (1972) reported no increase in the malformation rate in 64 newborns whose mothers had taken this drug during the first half of pregnancy. Spiramycin has been used extensively in Europe during the first trimester with no appar- ent adverse fetal effects. Sulfadiazine, a sulfonamide, has not been reported to be terato- genic when used in the first trimester. However, as with all sulfonamides, it could poten- tially be related to hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn, especially in the premature infant. The recommendations given in this section are derived from the author’s experience or opinion. Urinary tract infections Urinary tract infections are among the most common infections encountered in pregnant women (Duff, 1994).
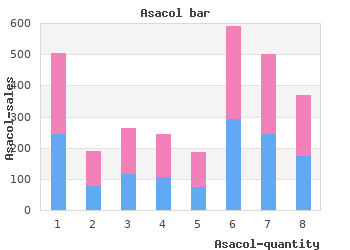
This is part of the calculation to determine how much blood is flowing through the left ventricle outflow tract with each heart beat buy asacol 400mg online. The other part of the calculation involves determination of the Velocity Time Integral using the apical five chamber view buy 400mg asacol otc. In the fourth row of images cheap asacol 400mg on-line, an apical five chamber view is Congestive Heart Failure – Andrew Patterson, M. The apical five chamber view can be used to calculate the Velocity Time Integral using pulse doppler imaging. On the left, the pulse doppler beam is directed in the line of the left ventricular outflow tract. On the right, a pulse doppler measurement is taken just proximal to the aortic valve and the Velocity Time Integral is calculated by determining the area under the curve. The left ventricle stroke volume can be calculated by multiplying the Cross Sectional Area of the left ventricle outflow tract and the Velocity Time Integral. The details of the measurements described in this figure legend are beyond the scope of this course. However, the idea that left ventricle preload and stroke volume/cardiac output can be easily determined using echocardiography should be appreciated (i. Increasing “preload” (1) will improve ventricular output in normal, hyperdynamic, and failing hearts within certain limits. Venodilators (4) and diuretics (5) can decrease ventricular volume by causing “pooling” of blood outside the central venous system and by reducing intravascular volume, respectively. Clinically, it is useful to plot “preload” versus ventricular output (the Starling relationship). By doing so, one can easily identify normal, hypodynamic, and hyperdynamic ventricular function. The inotropic state of the cardiac muscle as well as the “afterload” determines the Starling Curve on which the heart “moves. Thompson) presents to your clinic with shortness of breath that has become progressively more severe during the past month. Thompson reports that during the past month she developed an intolerance to lying flat and now requires four pillows to prop her head up when sleeping. She also describes fatigue that has worsened over the course of the past six weeks. She had been breastfeeding, but her fatigue and shortness of breath have forced her to transition the baby to formula feeds. Auscultation of the chest reveals bilateral crackles, a third heart sound, and a pansystolic murmur best heart at the apex consistent with mitral regurgitation. If you were to repeat the transthoracic echocardiogram, would you expect to see a difference in the wall motion or dimensions of the left ventricle compared to the prior examination? You decide to begin an infusion of dobutamine (an inotropic and afterload reducing agent). If you were to repeat the transthoracic echocardiogram once again, would you expect the wall motion of the left ventricle to change after institution of the dobutamine infusion? The pressure volume-loop (see Figure 8) diagrams the relationship between intraventricular pressure and volume throughout the cardiac cycle. The point of maximum volume and minimal pressure is located at the bottom right part of the loop (B). During the first part of the loop, pressure rises but volume remains constant (isovolumic contraction). When left ventricle pressure exceeds aortic root pressure, the aortic valve opens. At this point (C), ejection of blood from the ventricle begins and volume within the ventricle diminishes. When the ventricle reaches its maximum activated state (D), the aortic valve closes and isovolumic relaxation begins. Pressure-volume loops can be used to describe “preload,” compliance, “afterload,” and contractility (see Figure 9). Pressure-volume loops can be used to accurately depict clinically relevant information, such as stroke volume, “preload”, compliance, contractility, and “afterload. Changes in the pressure-volume loop that one might expect for a “volume-overloaded” heart failure patient are depicted. Jones) is going to be admitted to the Intensive Care Unit post-operatively after undergoing revision of a left total hip replacement. He has a history of coronary artery disease and is status post two myocardial infarctions during the past five years. His intraoperative course has been complicated by an acute 1500 mL blood loss and an episode of hypotension (80/40 mm Hg). The Anesthesiologist immediately administered two units of packed red blood cells, one unit of fresh frozen plasma, and 1. However, before these fluids could be administered the patient’s pulmonary artery pressures increased from 20/12 to 47/30 mm Hg. As the fluid was administered, the patient’s blood pressure initially increased to 120/70, and the ischemic changes resolved. Unfortunately, with the administration of two additional units of packed red blood cells and one unit of fresh frozen plasma, his blood pressure decreased again to 100/50.
9 of 10 - Review by R. Jens
Votes: 315 votes
Total customer reviews: 315