By Z. Hengley. Trinity College, Hartford Connecticut. 2018.
In our thesis work is planned to analyze the impact of personal qualities of the auditor on the principles best 4 mg singulair, methods and ways of auditing cheap singulair 5 mg amex, to make the expanded criteria for personality traits to be met by the auditor and propose a method of checking compliance with those criteria discount 4 mg singulair mastercard. The success and competitiveness depend on competent management decisions and the level of competence of the personnel that directly affects the quality of the end product of each company. High requirements are put forward for the competence of personnel who are engaged in various kinds of control. The auditors should pass appropriate training, traineeship and certification, maintain and improve their competence in this field of activity. The aim of our research was the development of the internal auditors training program and evaluation of their competence. As a result of conducted research a program for internal auditors training and assessing their practical work at the pharmaceutical company has been developed, which includes: selection plan (determination of the necessary professional skills and knowledge of potential auditors; criteria for evaluation and ranking of candidates (assessment of professional knowledge of candidates for auditors and their expertise rating on a 5- point scale); training program for internal auditors (list of lectures and practical exercises followed by evaluation of acquired knowledge); program to improve knowledge and skills (development plan); quality control program of internal auditors work after conducting audits at the enterprise (used the method of units workers questioning where the internal audit carried out). The program developed can be used in the preparation of internal auditors in the pharmaceutical enterprises. It allows assessing the skills and knowledge of potential auditors and train them to use the knowledge gained in practice. The program is aimed not only at the recruitment and training of auditors, but also to ensure the monitoring of their professional development. Today improve the competitiveness of domestic production enterprises is an urgent matter of national importance, because the economy is closely linked to increased requirements for product quality as one of the main factors ensuring the competitiveness of products and services in the developed world. To successfully run a business, you need to work on the rules of the world market not only in terms of production technology, but also in the management of the enterprise. Our research has focused on the issue of regulation of process «Control of monitoring and measuring devices». Development, implementation and certification of quality management system the company is not only demanding clients but also becomes a tool for optimizing internal processes, which in turn leads to higher product quality, reduce costs and increase in profits. Materials and methods: experimental and theoretical methods: logical analysis, the hypothetical synthesis of theoretical generalizations; empirical methods (observation, comparison). Internal results received by the organization from implementing a quality management system directly depend on the efforts it is making to improve its activity. External benefits the organization receives when certifies its quality management system by an independent competent authority for certification. Important elements of quality assurance is the production processes at the plant, each of which is characterized by a number of parameters which often involved measuring equipment. These settings should be changed only set limits to support the process in specified operating conditions and to provide relevant product characteristics. Metrological support system must solving measuring tasks, provide reliable information about production values processes. Obviously, the production efficiency and product quality level is largely determined by how efficiently the company uses information on the production process. A quality assurance and metrological support of production are interrelated and determine the required accuracy of all the properties and conditions at each stage of the production process. Metrological provision of production covers all stages of the product life cycle, from the stage of research and experimental development activities, including: analysis of measurements; establishing a rational range of measured values and the use of measuring instruments (working and reference) due accuracy; providing verification and calibration of measuring instruments (W); Development of methods of measurement for the standards of accuracy; metrological examination of design and technological documentation; implementation of necessary regulations (national, sectoral and enterprise standards); accreditation for technical competence of staff; metrological supervision. Current legislation in the field of metrology quality assurance requires all companies to control product quality during production, commodity, planning, and ensure efficient use of measuring instruments that are used. In addition, the law established the responsibility of heads of enterprises for the selection of the right measurement technology and for its timely verified. Metrological support system must solving measuring tasks, provide reliable information about production values processes. Most of the enterprises undertaken to organize and improve metrological support of production can be divided into two groups: Measures cover organizational issues related to the organization of work on performance measurement, creation of documentation for processing and use of the information received, ensuring the training of qualified personnel in the field of measurement and further improve their skills. In Ukraine diabetes occupies the third place on prevalence after cardiovascular and oncologic diseases. The purpose of work was creation self of the combined drugs, with diminished probability of origin of side effects. Composition for medication, that it was created in the process of previous researches it was subject to the expert estimation, in relation to side effects. These methods allowed us to educe most critical components in the process for create of drug. By the method of expert evaluation it was chosen those the values of which were evened, whether were more than 100. Dyspepsia disorders had most disparity, namely, nausea, loss of appetite, pain in epigastrium and metallic taste in an oral cavity. The way in which bacterial cells adhere to surfaces, or within communities, is of great importance to pharmaceutical microbiologists. Russ, adhesion is the binding force between two different materials, whereas cohesion is the binding force between two similar materials. When two materials are brought into contact with each other, the surface molecules interact, giving rise to attractive forces that may be physical and chemical (e. Physical bonding: Physical bond consist four types of theory: mechanical interlocking, diffusion theory, adsorption and electrostatic. Adsorption theory is a form of adhesive bonding involving the attraction between the molecules of an adhesive and a surface material. The bonding of an adhesive to an object or a surface is the sum of a number of mechanical, physical, and chemical forces that overlap and influence one another. As it is not possible to separate these forces from one another, we distinguish between mechanical interlocking, caused by the mechanical anchoring of the adhesive in the pores and the uneven parts of the surface, electrostatic forces, as regard to the difference in electro negativities of adhering materials, and the other adhesion mechanisms dealing with intermolecular and chemical bonding forces that occur at the interfaces of heterogeneous systems. Chemical bonding: is a form of adhesive bonding involving a reaction that results in covalent bonds between the molecules of the adhesive and the surface material. The chemical bonding mechanism suggests that primary chemical bonds may form across the interface. In chemical bond consist two category of bond which is primary and secondary bond.
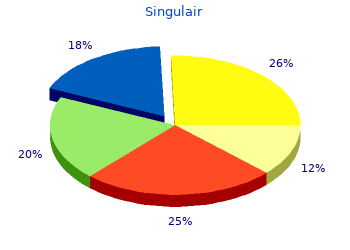
In another economically developed country - Germany - also dominates the action in-house labor market discount singulair 4mg amex. The idea is that investment in education and at the societal level and on a personal level is the most advantageous placement of capital order 4 mg singulair with mastercard. Pay off long-term costs and high dividends discount singulair 4 mg visa, and there is a direct correlation: the cost - the level of education – income. We reviewed the particular in-house training of staff on the example of the five developed countries. In-house training is defined in these countries as one of the leading trends in the youth and adult population, helping people to successfully solve the social problem of employment. The study of the theory and practice of professional functioning of foreign public education system in-house allows us to conclude that this system is usually an integral part of the internal labor market (hidden labor market within the enterprise). In-house training serves as a mechanism for employers of these countries to extinguish the social contradictions within the company, that is, try to do without the mass release of staff to the external labor market through retraining, permutation (rotation), training of existing staff, the introduction of advanced, cutting-edge technologies. Concluding the brief analysis of international experience in-house training of staff in the context of the various aspects, we emphasize that many of the positive aspects (as well as domestic experience) has been successfully implemented in modern major pharmaceutical companies, firms, enterprises. The study of the theory and practice of vocational training of the population considered foreign operation intra-system leads to the conclusion that this system is usually an integral part of the internal labor market (hidden labor market within the enterprise). In-house training population serves as a mechanism for employers of these countries to extinguish the social contradictions within the enterprise, that is, try to do without the mass release of staff to the external labor market through retraining, permutation (rotation), training of existing staff, the introduction of advanced, cutting-edge technologies. On the one hand, distance learning in this context - is training of employees in the workplace, ie, in the firm, and on the other - it is learning by using Internet technology, and teachers, by tutors are experts who are well beyond the scope of this company, city, region. Distance learning is an educational technology is a combination of in-house and external training, members of the corporate training structure, which is realized at the expense of companies, firms, corporations, companies, etc. Today almost every profitable company that wants to compete and grow their business critical condition for achieving sustainable success is adherence to this principle. In the course of our work examined different approaches to establishing a system of feedback and increase customer loyalty in enterprises of various fields and traced change the standards for quality management system and analyzes the typical violations of the requirements observed in the domestic pharmaceutical enterprises. We offered must regulate activities related to the interaction with consumers of feedback. In practice, these actions are not often described in the documents of the reasons why the procedure contains important elements and cannot regulate and perform activities that could significantly affect the outcome of the process. For example, the lack 249 of description of the performance evaluation process of interaction with consumers (and any other process) makes it impossible to accumulate measurable results of assessments and track them over time, analyzing trends and patterns. In addition, the lack of data makes factual basis for the development of corrective and preventive actions needed for continuous improvement process. The same can be said about the importance of regulated planning phase of the process, because proper planning any activity largely determine sits out come. Information communication with customers, described documented procedure should include: a) provide information about products/services; b) processing requests, contracts or orders, including their changes; c) provide feedback on products and services from consumers, especially for claims, complaints or claims of consumers; d) handling or property management customers; e) establish special requirements for actions taken in unforeseen circumstances. The organization has always define the requirements established customer, including requirements related to delivery and subsequent maintenance, if applicable to the products. In addition, should also be determined by the requirements not stated by the customer but necessary for specified or intended use, where such knowledge. We believe that organizations often make the mistake of only limited documentation of direct regulatory or customer requirements, without describing those that are not obvious. This element should include ways and means of receipt of such information, as well as enough detailed sequence of actions in such situations - from receipt, registration and consideration of complaints, to develop appropriate solutions and actions to eliminate the causes of complaints and minimize the negative consequences for the customer and its information. Documented procedures also describe the monitoring data relating to customer perception of the degree of their needs and expectations. It is necessary to determine the methods for monitoring and analyzing this information. For example, this may include consumer surveys, reviews of products delivered / services rendered, meetings with customers, market share analysis, and thanks for warranty claims and dealer reports. Also organization shall meet requirements for post-delivery activities associated with the products and services. In determining the extent of post-delivery activities that are required, the organization shall consider statutory and regulatory requirements; the potential undesired consequences associated with its products and services; the nature, use and intended lifetime of its products and services; customer requirements; customer feedback. Post-delivery activities can include actions under warranty provisions, contractual obligations such as maintenance services, and supplementary services such as recycling or final disposal. The feature of modern pharmaceutical market is the constant growth of competition, incessant rise in prices for pharmaceutical products from suppliers and yet consumers do desire to keep prices at a reasonable level. In order to fulfill the social mission of pharmacy, and commercial gain, pharmacies are searching for ways to increase competition and optimization work. Our research has focused on the issue of introduction of Quality Management Systems in the work of pharmacies and pharmaceutical companies. We used empirical methods: observation and comparison; and methods of experimental and theoretical: logical analysis, the hypothetical synthesis of theoretical generalizations. Providing quality pharmaceutical care in sufficient quantity and adequate quality, according to the expectations of the consumer (by pharmacies, patient or doctor) requires solving complex strategic problems of quality control of pharmaceutical care. The activities of the pharmaceutical providing of population conducted in the following areas: improve the system of quality assurance of pharmaceutical care management solutions optimal balance between social and economic performance of pharmacy; improve the quality of pharmaceutical care by analyzing the shortcomings of consultation with experts; optimization of partnership with consumers of pharmaceutical services: surveys, analysis of feedback and requests, analyzing complaints and applications customers, the organization benefits for some sectors of the population and hotline for consumers; corporate approach to improving cost-effectiveness of pharmaceutical care. The quality of pharmaceutical care is ensured through systematic approach and objective assessment of each element that make up the system: quality policy, the 251 responsibility of the head, staff and authorized persons of quality control of drugs, experience of employees and the company as a whole, the level of economic development, document processes and document management , management information quality; skills development, internal audits and others. Quality Management System to enable domestic companies entering foreign pharmaceutical market, attracting foreign investors, joint projects with foreign firms and prestige in the domestic and international level. Quality management – quite expensive process involving qualified personnel, quality infrastructure and working environment, good governance, the right business processes, and thus higher customer satisfaction, and as a result of good financial results. The introduction of quality management in pharmaceutical organizations require commitment, labor costs, economic costs psychophysical costs and awareness goals of quality management development of which requires a certain sequence and phasing (according to the Deming cycle).

For example order singulair 10 mg online, insulin at pH 7 exists predominantly as hexameric aggregates order singulair 4mg online, which are too large to be absorbed purchase 10mg singulair. Proteins tend to undergo denaturation in vitro, the rates of interfacial denaturation are strongly dependent on the specific protein and on such solution properties as temperature, pH and salt concentration. For example, human growth hormone undergoes only limited, and fully reversible, denaturation between pH 1. Various approaches have been attempted to prevent loss of protein by adsorption to glass and plastic, including treating surfaces with proteins such as bovine serum albumin, fibrinogen and ovalbumin, or modifying the solvent by adding surfactants or glycerol. Potential peptide and protein drugs are subject to degradation by numerous enzymes or enzyme systems throughout the body. Small peptides are relatively resistant to the action of endopeptidases but their activity is significant for large peptides. By considering these features, the enormous difficulties associated with overcoming the enzymatic barrier to peptide and protein delivery should be apparent. Degradation usually occurs at the site of administration and is possible in every anatomical site en route to the target receptor. Furthermore, protecting a single bond on a peptide or protein drug from a particular type of enzyme is insufficient to confer protection on the entire drug from enzymatic hydrolysis—other enzymes may attack the protected bond and the other unprotected bonds on the drug are still vulnerable. Several methods of modifying peptide structure to improve metabolic stability have been investigated, including: • substitution of an unnatural amino acid in the primary structure; • introduction of conformational constraints; • reversal of the direction of the peptide backbone; • acylation or alkylation of the N-terminus; • reduction of the carboxy-terminus; formation of an amide. However, even extensive modifications of peptide structure can only afford relative, rather than absolute, protection from enzyme attack. In the gastrointestinal tract, the enzymatic barrier is probably the most significant obstacle to the successful oral delivery of peptides and proteins, as demonstrated by the following observations: • The rate of hydrolysis of peptides is inversely related to the amount transported across the intestine. Luminal activity from the pancreatic proteases trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase and carboxypeptidase A is mainly directed against large dietary proteins. The main enzymatic activity against small bioactive peptides is derived from the brush border of the enterocyte. Intracellular degradation is most specific against di-peptides and occurs mainly in lysosomes, but also in other intracellular organelles. In comparison to the oral route, much less is known about the nature of the enzymatic barrier to therapeutic peptides and proteins in alternative routes such as the buccal, nasal, pulmonary, dermal and 36 vaginal routes. As a first step in characterizing the proteolytic barrier, the proteolytic activity in various mucosal tissues can be determined by incubating a peptide or protein in epithelial tissue homogenates. However, care should be exercised in interpreting studies of this kind as peptides are often exposed to a wide range enzymes, including both extra- and intracellular enzymes, present in a homogenate of epithelial tissue. The actions of intracellular enzymes will not be significant if the peptide is absorbed by the paracellular route, never coming into contact with the inside of the cell. Studies on characterizing the enzymatic barrier at each delivery site have investigated the pattern of cleavage of enkephalins, substance P, insulin and proinsulin, and have demonstrated the presence of both exo- and endo-peptidases in the various epithelial tissues. What distinguishes one route from another is probably the relative proportion of these proteases, as well as their subcellular distribution. Absorption barriers Absorption barriers to peptides and proteins arise from the enzymatic barrier described above and also from the physical barrier properties of the epithelium, arising from the hydrophobic membranes and tight intercellular junctions. The physicochemical properties of peptide and protein drugs generally make them unsuitable for absorption by any of the possible routes and mechanisms described above. For example, these molecules are generally too large for transport via the paracellular route, unless the integrity of the tight junctions is disturbed by the use of penetration enhancers. Similarly, passive diffusion across lipidic membranes, the major route of absorption for conventional drug molecules, is also generally not possible, as the molecules tend to be too large and too hydrophilic to penetrate the lipidic membrane barrier. Again, the use of appropriate penetration enhancers can potentiate absorption via this route. Research is also being directed towards increasing the lipophilicity of these moieties, to enhance transport via this route. Active transport mechanisms exist in the gastrointestinal tract and other epithelial sites, for the absorption of di- and tri-peptides. As described above, a greater understanding of the molecular specificity of this carrier could provide important leads for the delivery of peptides. Proteins and large peptides may be transported across cells via endocytic processes. Transcytosis is achieved if the endocytic vesicles can reach the basal membrane without fusion with lysosomes. However, various studies have shown that in the majority of cases the internalized protein is degraded, indicating that the transcytotic pathway is a minor one and most of the endocytosed protein is subject to lysosomal degradation. Unwanted distribution may also cause toxic side-effects resulting from drug action at non-target sites. Premature excretion may arise if small, highly potent, therapeutic peptides are cleared rapidly through the kidneys, before reaching the target site. For optimal drug therapy, drug delivery systems must tailor drug input in response to such factors as: 37 • circadian and other rhythms of predictable period; • modulations on a minute-to-minute basis, in response to such factors as nutrient delivery, physical activity and metabolic stress; • the pulsatile release patterns of many endogenous peptides and proteins; • the complex feedback control mechanisms which affect the release and biological effects of many endogenous peptides and proteins 1. However, nucleic acid-based biopharmaceuticals are now becoming increasingly important therapeutic entities. Research into nucleic acid-based therapeutics is currently focused in two main areas: • gene therapy; • oligonucleotide therapy. This whole field is still at a largely experimental stage, but holds great potential to revolutionize the treatment and prevention of disease if safe and effective delivery vectors can be found. The delivery of nucleic acid based-therapeutics is the subject of Chapter 14; the following discussion comprises a brief introduction to gene therapy.
This series of events occurs readily in herpesvirus-infected tissues but poorly in normal tissues discount singulair 4mg without prescription, since the initial phosphorylation is accomplished mainly by a herpesvirus-specific deoxynucleoside (thymidine) kinase (Elion 10mg singulair overnight delivery, 1983; Laskin order 10 mg singulair with amex, 1984; King, 1988). The aci- clovir triphosphate is formed readily and is more persistent than the parent compound, remaining for several hours in cultured cells. When taken orally, the drug is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with a reported bioavailability of 15–30%, owing to its limited solubility in an aqueous environment; therefore, intravenous dosing is considered more effective (O’Brien & Campoli-Richards, 1989). The drug is widely distributed throughout the body and has been found in plasma, kidney, lung, liver, heart, vagina, brain, cerebrospinal fluid, aqueous humor, saliva and skin (Laskin, 1983; de Miranda & Blum, 1983; Rogers & Fowle, 1983; Brigden & Whiteman, 1985; O’Brien & Campoli-Richards, 1989; Vergin et al. After oral doses of 200 mg taken four to five times daily or 400 mg taken two to three times daily, the peak plasma concentration is about 2 μmol/L (0. After oral administration, the amount of aciclovir in the kidney and lung was actually higher than that in plasma, while the concentration in cerebrospinal fluid was half of that in plasma (Blum et al. After topical administration, the epidermal concentration of aciclovir was enhanced 48-fold over that observed after oral dosing, but the delivery of the drug to viruses replicating in the basal epidermis was considerably less efficient (Parry et al. The pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered aciclovir has been described best by a two-compartment open model (Laskin, 1983; Rogers & Fowle, 1983; O’Brien & Campoli-Richards, 1989). The binding of aciclovir to plasma protein has been reported to be 9–33%; the peak concentrations in plasma are typically achieved within 1. After intravenous dosing with aciclovir, 45–75% of the drug is excreted in the urine as unchanged compound, but after oral dosing this percentage is reduced to 14–22%, with a large fraction appearing in the faeces (Laskin, 1983; de Miranda & Blum, 1983; Vergin et al. Two minor urinary metabolites, 9-carboxymethoxy- methylguanine and 8-hydroxy-9-(2-hydroxyethyl)guanine, have been reported to constitute 8–14% and about 0. Active renal clearance occurs by glomerular filtration and renal tubular secretion, with a half-time of 2–3 h (Laskin, 1983; O’Brien & Campoli-Richards, 1989) and a clearance rate of 3. In patients with renal impairment, the mean elimi- nation half-time can be extended to 20 h, and the total body clearance rate can be decreased 10-fold; it is therefore necessary to reduce the dose accordingly (de Miranda & Blum, 1983; Rogers & Fowle, 1983; Brigden & Whiteman, 1985; O’Brien & Campoli-Richards, 1989). Transplacental pharmacokinetics A 39-year-old pregnant woman, presumed to be at 30 weeks of gestation, was treated with aciclovir (350 mg, or 15 mg/kg bw) intravenously every 8 h throughout the remainder of gestation. Beginning at week 38 of gestation and continuing until delivery, seven women were treated orally with 200 mg aciclovir every 8 h and eight with 400 mg aciclovir every 8 h. The drug appears to be taken up efficiently by many tissues, including the brain and skin (de Miranda et al. Like humans, dogs, rats and rhesus monkeys show a biphasic decline in the plasma concentration of aciclovir, indicating a two-compartment open model, with a half-time of 1–3 h (de Miranda et al. Gastrointestinal absorption was poor in the 8-week-old rats, with a bioavailability of 7. Absorption of aciclovir in the gastrointestinal tracts of the young rats was shown to occur by an efficient passive diffusion process, which apparently becomes inefficient at the time of weaning (Fujioka et al. Beagle dogs given 20 mg/kg bw aciclovir had a mean peak plasma concentration of 42 μmol/L (10 mg/L) by 1. The body clearance was similar to the glomerular filtration rate, indicating the absence of active tubular secretion (de Miranda et al. Skin absorption occurred by a first-order process which resulted in excretion of about 0. When aciclovir is given orally, the doses are typically low and serious adverse events are extremely rare (Goldberg et al. Oral dosing is less frequently neurotoxic but was reported to induce acute disorientation in four patients, three of whom had renal insufficiency (MacDiarmaid-Gordon et al. Renal dysfunction is not an absolute requirement for aciclovir-induced neurotoxicity; but, apart from age and neurotoxic medications (Rashiq et al. The neurotoxicity induced by aciclovir manifests primarily as tremor (28–30%), myclonus (30%), confusion (30–43%), lethargy (17–30%), agitation (27–33%) and hallucination (20–26%) (Rashiq et al. Less frequent manifestations (3–17%) include dysarthia, asterixis, ataxia, hemipares- thaesia and seizures (Ernst & Franey, 1998). Neurotoxicity typically occurs during the first 24–72 h of drug administration, and discontinuation of the drug results in a complete return to normal by about 15 days (Rashiq et al. Haemodialysis has been shown to attenuate aciclovir-induced neurotoxicity effectively in symptomatic patients (Krieble et al. In patients receiving high doses of aciclovir, reversible increases in serum creatinine concentrations can occur (Kumor et al. The existence of compromised renal function, use of other nephrotoxic drugs, rapid infusion of large doses, advanced age and dehydration can all contribute to aciclovir-induced nephrotoxicity (Rosenberry et al. Like aciclovir-induced neurotoxicity, the nephrotoxic effects are typically transient and rapidly ameliorated by haemodialysis (Whitley et al. Topical adminis- tration may be associated with pain, burning or rash (Rosenberry et al. The main effect observed is related to kidney function but is dependent on dose, animal strain and route of administration. Wistar rats given three subcutaneous injections of 15 mg/kg bw aciclovir per day for five days (a total of 45 mg/kg bw per day) showed no significant changes (Hannemann et al. Obstructive nephropathy, caused by crystalline precipitation of the drug in the renal tubules and collecting ducts, was observed in Long-Evans rats given intravenous injections of 20, 40 or 80 mg/kg bw aciclovir daily for three weeks. These changes were accompanied by increased water consumption, urine output, blood urea nitrogen concentration and kidney weight (Tucker et al. All of the nephro- toxic effects of aciclovir resolved within two weeks after drug discontinuation. In Sprague-Dawley rats given 50, 150 or 450 mg/kg bw aciclovir per day by gavage for 25 months, no treatment-related toxic effects were observed (Tucker et al. Taken together, these studies suggest that nephrotoxicity is much more likely to result from intravenous than from oral dosing with aciclovir. Parallel clinical observations support the notion that oral dosing is less toxic than intravenous infusion in humans. Beagle dogs given rapid intravenous injections of 10, 20, 25, 50 or 100 mg/kg bw aciclovir twice a day for one month showed marked dose-related toxic effects, including death, at the two higher doses.
9 of 10 - Review by Z. Hengley
Votes: 219 votes
Total customer reviews: 219